1. Diffuse erosion
Diffuse erosion corresponds to particles detachment by rainfall (« splash »). It corresponds to the product of runoff and the suspended particles concentration in runoff water, calculated according to the surface condition of the soil and the maximum rainfall intensity (generally calculated at a 6-minutes time step) (Cerdan et al., 2002) :
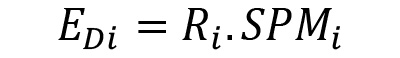
With :
EDi : diffuse erosion (kg)
Ri : runoff (m3)
SPMi : SPM (Suspended Particulate Matter) concentration in runoff water (g/l)
2. Concentrated erosion
Concentrated erosion occurs when the specific peak flow QSi (m3/m/s) exceeds a critical discharge QCRITi (m3/m/s), defined as a model parameter. When the condition is met, the concentrated erosion appears in the form of a single gully per mesh. Concentrated erosion is calculated according to one of the two modules proposed in the model.
« Empirical » module
The gully section is assumed to be rectangular. The gully width WGi (m) is determined according to the empirical equation developed by Nachtergaele et al. (2002):
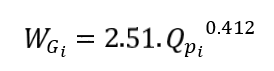
The runoff velocity in the gully VGi (m/s) is then calculated using the empirical equation of Govers (1992) :

The gully height HGi (or incision height) is deduced from the gully width WGi, the flow velocity VGi and the peak flow QPi. The height is weighted according to the soil erodibility ERODi (the factor varies between 0 and 1, with 0 for non-erodible soil and 1 for highly erodible soil) :
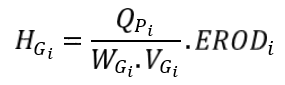
The gully volume VOLi (m3) s determined according to the equation :
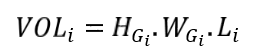
With :
Li : cell resolution (m)
The concentrated erosion ECi (kg) is obtained by multiplying the volume of the gully VOLi by the density of the soil rho, arbitrarily defined as 1400 kg/m3.
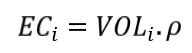
Total erosion is the sum of diffuse and concentrated erosion.
Module « KSV »
Concentrated erosion ECi (kg) is calculated as the product of erodibility ERODi (-), the local slope Si (%) and runoff volumeVi (m3) :
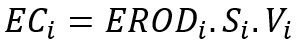
3. Transfer and deposition
Erosion is accumulated from upstream to downstream along with runoff (hereafter refered to « sediment flow »). Sediment is deposited when the runoff reinfiltrated or when the runoff SPM concentration exceeds the SPM transport capacity.
In the case of reinfiltration, the sediment mass deposited is calculated according to the following equation :

With :
DIi : sediment deposition (kg)
Ii : infiltration (m3)
SPMi : SPM concentration in runoff (g/l)
The SPM concentration at the transport capacity SPMTCi (g/l) is defined according to the following equation :

With :
a, b : parameters (-)
Si : local slope (%)
ni : Manning’s coefficient (s.m-1/3)
The sediment mass deposited if the transport capacity is exceeded, DTCi (kg), is determined according to :
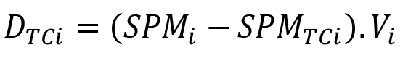
With :
Vi : runoff volume (m3)
