To parameterize the WaterSed model, land use, runoff axis and soil maps are combined. For each of the resulting maps combination, the hydrodynamic (infiltration capacity, imbibition, etc.) and erosive (erodibility, etc.) properties that can be used by the model are calculated.
1. Principle
To define the properties of each combination, CODE_LU and CODE_SOIL are concatenated to form a new CODE.
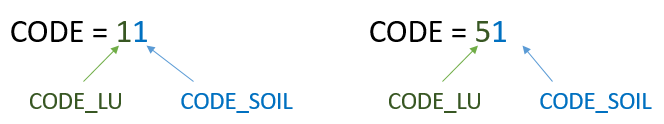
A CODE of 11 corresponds to a winter crop on a loamy soil, and a CODE of 51 corresponds to a potato crop on a loamy soil. This technique provides a unique identifier for each combination. Hydrodynamic and erosive properties will be defined for each of these values.
Launch SAGA GIS. Open button and point toward the propriete_hydrosed_occsol.txt file.
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/REGLES/propriete_hydrosed_occsol.txtClick on Open in the right-hand bottom of the window. Right-click on the table then Show.
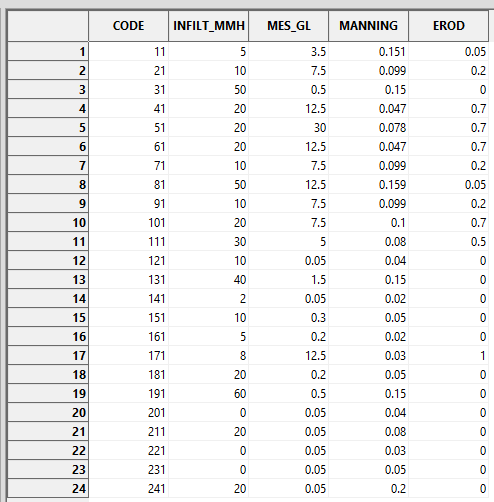
Each CODE is characterized by an infiltration capacity (INFILT_MMH), a SPM concentration in runoff (SPM_GL), a Manning’s ratio (MANNING) and an erodibility (EROD).
Note: The CODE and resulting values (e.g. INFILT_MMH) must be adapted according to the study site and the type of rainfall event.
To generate the 4 corresponding grids for infiltration capacity, SPM concentration, Manning’s coefficient and erodibility, simply reclassify the CODE according to this table.
This reclassification is carried out using the Inputs Generator tool, presented later in this tutorial.
2. Inputs Generator
2.1. Operating
The Inputs Generator automatically generates the 4 property grids from the 3 shapefile maps of land use, runoff axis and soil, and the table of hydrodynamic and erosive properties. These grids are generated in DTM Grid Sytem.
Le fonctionnement de Input Generator est décrit suivant le schéma suivant.

Note: after converting the land-use and runoff axis maps into a grid according to CODE_LU, the two grids are combined by replacing the land use CODE_LU with the axis CODE_LU at the axis locations.
The tool also generates the 4 other grids used to define rainfall characteristics and initial soil moisture (described in a dedicated tutorial).
2.2. Interface description
The Inputs Generator tool can be accessed from the Download tab and is contained in the WaterSed.zip zip file. If you follow the correct tutorial order, you’ll find it in TUTORIAL/MODELE. It is called WS_INPUT_v1.2.xml. Install the tool by dragging and dropping the xml file into the SAGA GIS Tools window.
Launch the Inputs Generator tool from :
Tools tab<> Tool Chains <> WaterSed <> Inputs Generator
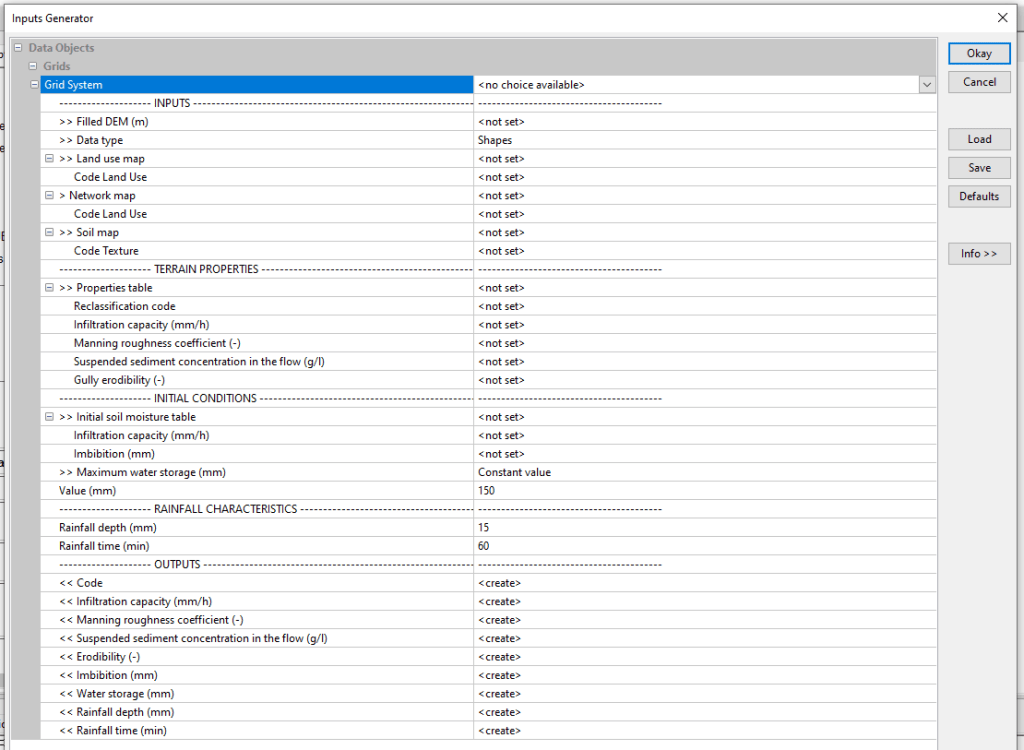
The tool is organized into menus to structure input and output data. Input data are divided into 4 menus: INPUTS, TERRAIN PROPERTIES, INITIAL CONDITIONS and RAINFALL CHARACTERISTICS. The tool’s output grids are all grouped together in the OUTPUTS menu.
INPUTS menu
- Filled DEM :Digital Terrain Model (DTM) with hydrological correction
- Data type : format of land use, runoff axis and soil maps. Two scenarios:
Case 1 (Shapes) :the maps are in shapefile format, with a CODE_LU (Land Use Code) field in the attribute table for land use mapping, a CODE_LU field in the attribute table for runoff mapping and a CODE_SOIL (Texture Code) field in the attribute table for soil mapping.
- Land use map : land use mapping
- Code Land Use : attribute table field corresponding to the CODE_LU
- Network map (optional) : runoff axes mapping
- Code Land Use : attribute table field corresponding to the CODE_LU
- Soil map : soil mapping
- Code Texture : attribute table field corresponding to the CODE_SOIL
Case 2 (Grid) : the 3 shapefiles have been transformed into a grid according to the field CODE_LU and CODE_SOIL.
- Land use map : land-use mapping described according to the CODE_LU
- Network map (optional) : land-use mapping described according to the CODE_LU
- Soil map : land-use mapping described according to the CODE_SOIL
TERRAIN PROPERTIES menu
- Properties table : table .txt detailing the values for infiltration capacity, Maninng coefficient, SPM concentration and erodibility for each CODE
- Reclassification Code : column where CODE values are stored
- Infiltration capacity (mm/h) : column where infiltration capacity values are stored
- Manning roughness coefficient (-) : column where Manning’s coefficient values are stored
- Suspended sediment concentration in the flow (g/l) : column for storing SPM concentration values in runoff water
- Erodibility (-) : column where erodibility values are stored
INITIAL CONDITIONS menu
- Initial soil moisture table : table .txt detailing imbibition values for each infiltration capacity value
- Infiltration capacity (mm/h) : column where infiltration capacity values are stored
- Imbibition (mm) : column where imbibition values are stored
- Maxmimum water storage (mm) : maximum water storage capacity of the soil. This capacity can be determined using three methods :
Method 1 – Constant value : maximum soil water storage capacity constant over the entire basin. In this case, specify the value in Value (mm).
Method 2 – IBK method : maximum soil water storage capacity determined using the IBK method (detailed in the tutorial on rainfall and initial soil moisture). Specify minimum (Minimum water storage (mm)) and maximum (Maximum water storage (mm)) values.
Method 3 – Distributed : the user has a shapefile map of the soil’s maximum water storage capacity. Specify the shapefile in the Soil map line and the Water storage (mm) field.
RAINFALL CHARACTERISTICS menu
- Rainfall depth (mm) : total rainfall for the event
- Rainfall time (min) : effective duration of the event
OUTPUTS menu
- Code : CODE concatenated from CODE_LU and CODE_SOIL
- Infiltration capacity (mm/h) : limit value for the infiltration rate if the soil is saturated and homogeneous (continuous loss); this infiltration rate depends in particular on the texture and structure of the soil;
- Manning’s roughness coefficient : coefficient reflecting friction forces at the soil surface, as a function of soil roughness and vegetation cover ;
- Potential sediment concentration in the flow (g/l) : SPM concentration in runoff water (g/l); soil sensitivity to splash effect;
- Erodibility (-) : soil erodibility (value between 0 and 1); soil susceptibility to erosion due to runoff ;
- Imbibition (mm) : initial loss before the onset of runoff; imbibition is a function of soil texture and structure, but also of initial soil moisture;
- Water storage (mm) : maximum height of water equivalent to total filling of soil porosity; a function of soil thickness and porosity ;
- Rainfall depth (mm) : total height of rain event
- Rainfall time (min) : actual duration of the event
Note: all data requested must be filled in, except for runoff axis mapping, which is optional (example of a model based on a crop block with no runoff axis).
2.3. Application to case study
Import occ_sol.shp, axe_ruissellement_modif.shp, sol.shp , mnt_fill.sgrd , propriete_hydrosed_occsol.txt and regle_imbibition.txt files.
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/OCC_SOL/occ_sol.shp
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/OCC_SOL/sol.shp
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/REGLES/propriete_hydrosed_occsol.txt
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/REGLES/regle_imbibition.txt
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/TOPOGRAPHIE/mnt_fill.sgrd
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/TOPOGRAPHIE/axe_ruissellement_modif.sgrdLaunch the Inputs Generator tool and fill in the various layers requested.
Leave the default values in the INITIAL CONDITIONS and RAINFALL CHARACTERISTICS menus (these menus are described in detail in the tutorial on rainfall and initial soil moisture). Enter the Initial soil moisture table and the two associated fields. Click on Okay.

The 9 grids produced appear in the Data tab, then Data, Grids. To view a grid, right-click then Add to Map.
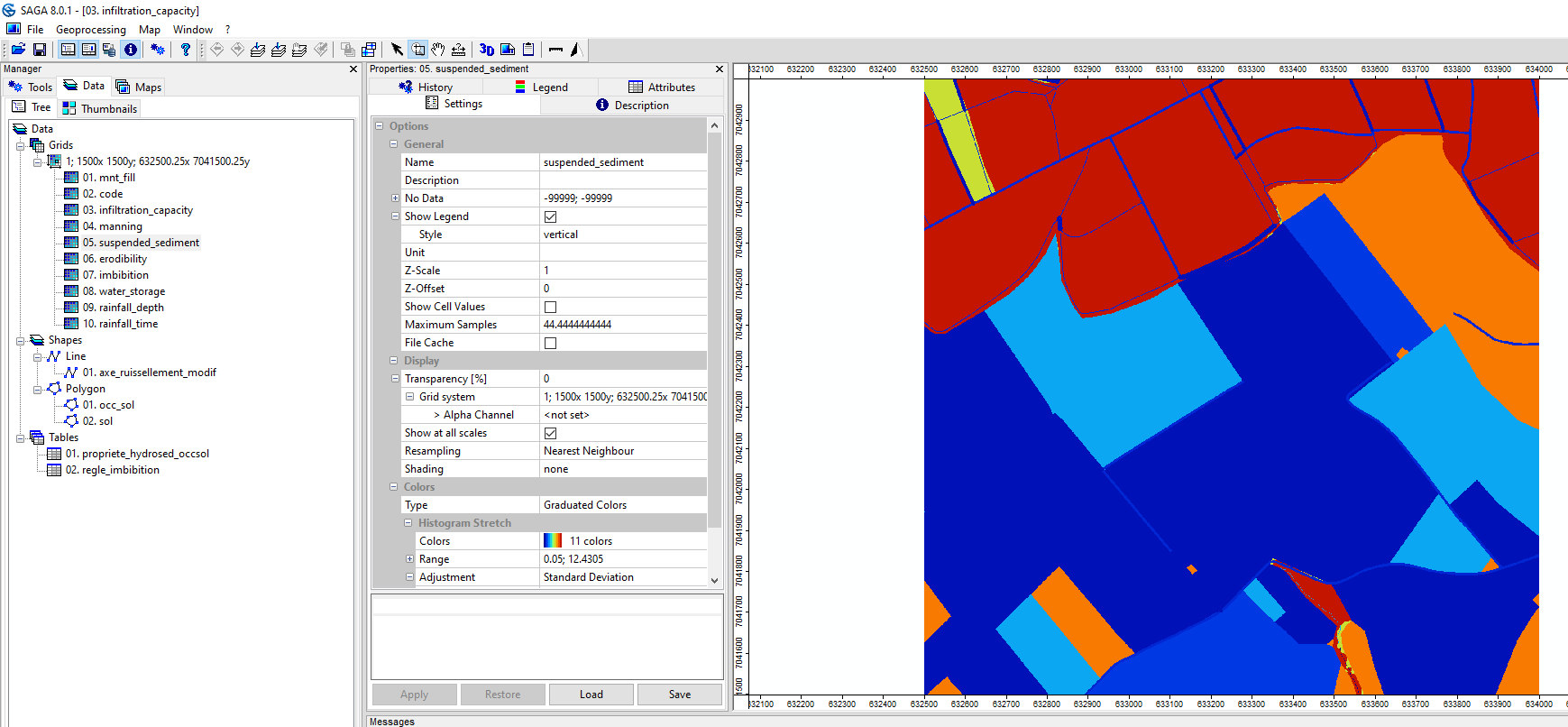
Save the code.sgrd, infiltration_capacity.sgrd, manning.sgrd, suspended_sediment.sgrd and erodibility.sgrd grids in the INPUT folder. The other grids were produced during the tutorial on rainfall and initial soil moisture.
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/INPUT/code.sgrd
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/INPUT/infiltration_capacity.sgrd
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/INPUT/manning.sgrd
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/INPUT/suspended_sediment.sgrd
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/INPUT/erodibility.sgrd
