Note : Before strating this tutorial, you must have completed the tutorial WaterSed Input Generator.
1. Principle
Soil water storage capacity corresponds to the maximum height of water that the soil can infiltrate. In the absence of soil data, a geomorphological method was applied to estimate these heights, based on concepts developed in the TOPMODEL model (Beven and Kirkby, 1979). The authors consider that the depth of the saturated zone is infinite and that the piezometric level of the water table controls the height of water that can infiltrate into the soil profile (Sivapalan et al., 1997). On a slope, the water head is highest at the top of the slope and lowest at the bottom, where the water table outflows at stream level.
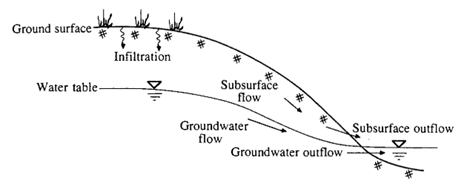
Schematic cross-section of a slope and the various groundwater flow processes
(Chow, 1988)
To spatialize this soil water storage capacity, the Index proposed by Beven and Kirkby (IBK) as topographic wetness index can be used. It is expressed as follows:
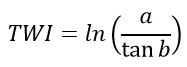
With :
TWI : Topographic Wetness Index
a : contributive area (m²)
b : local slope (radian)
The values are then normalized between 0 and 1 and inverted so as to have 1 values at the top of the slope and 0 values at the bottom. These values are finally normalized between two minimum and maximum soil water storage capacity limits :
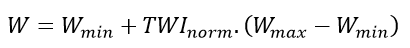
With :
W : soil water storage capacity (mm)
Wmin : minimum soil water storage capacity (mm)
Wmax : maximum soil water storage capacity(mm)
TWInorm : topographical humidity index standardized between 0 and 1.
Minimum and maximum limits are generally obtained from soil thickness mapping.
2. Use of Water Storage Generator
Launch SAGA GIS
Import the mnt_fill.sgrd grid (produced during the topography tutorial).
Import the infiltration_capacity_mmh.sgrd grid (produced during the WaterSed Input Generator tutorial).
Download Water Storage Generator (WS_WATER_STOR_v1.2.xml) from the Download tab and install the tool on SAGA GIS by dragging and dropping the xml file. The tool can be accessed from :
Tools <> Tool Chains <> WaterSed <> Water Storage Generator
The tool can generate a soil water storage capacity grid using two methods:
- Constant Value : unique value for soil water storage capacity
- IBK Method : soil water storage capacity values using the IBK method described above
Load mnt_fill.sgrd Grid System. In the DEM menu, point to mnt_fill. In the Infiltration capacity (mm/h) menu, point to infiltration_capacity_mmh. Enter a value of 50 for Minimum water storage (mm) and 110 for Maximum water storage (mm). Click on Okay.
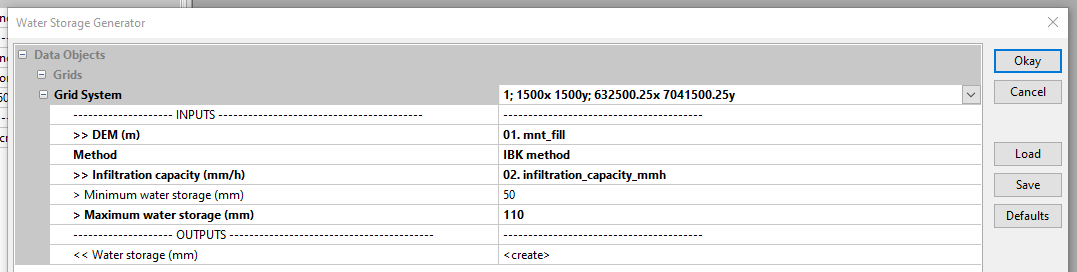
The resulting grid appears in the Data tab under the name Water storage (mm). To view the grid, right-click then Add to Map.

The blue zones are located at the bottom of the talweg and correspond to areas where the soil’s water storage capacity is close to 50. Zones from yellow to red are located on the upper slopes and correspond to areas where the soil’s water storage capacity is close to 110.
Save the Water storage (mm) grid under the name water_storage in the INPUT file.
/TUTORIEL/PREPROCESSING/DATA_BASE/water_storage.sgrd
